Quartz Rod UV Sensor
This is a UV sensor that is made out of a quartz rod, an aperture, and some electrical components. This device was designed and built by myself and used at my work to measure the intensity of high-power UV lights that we had set up in a tube format.
Features and Components
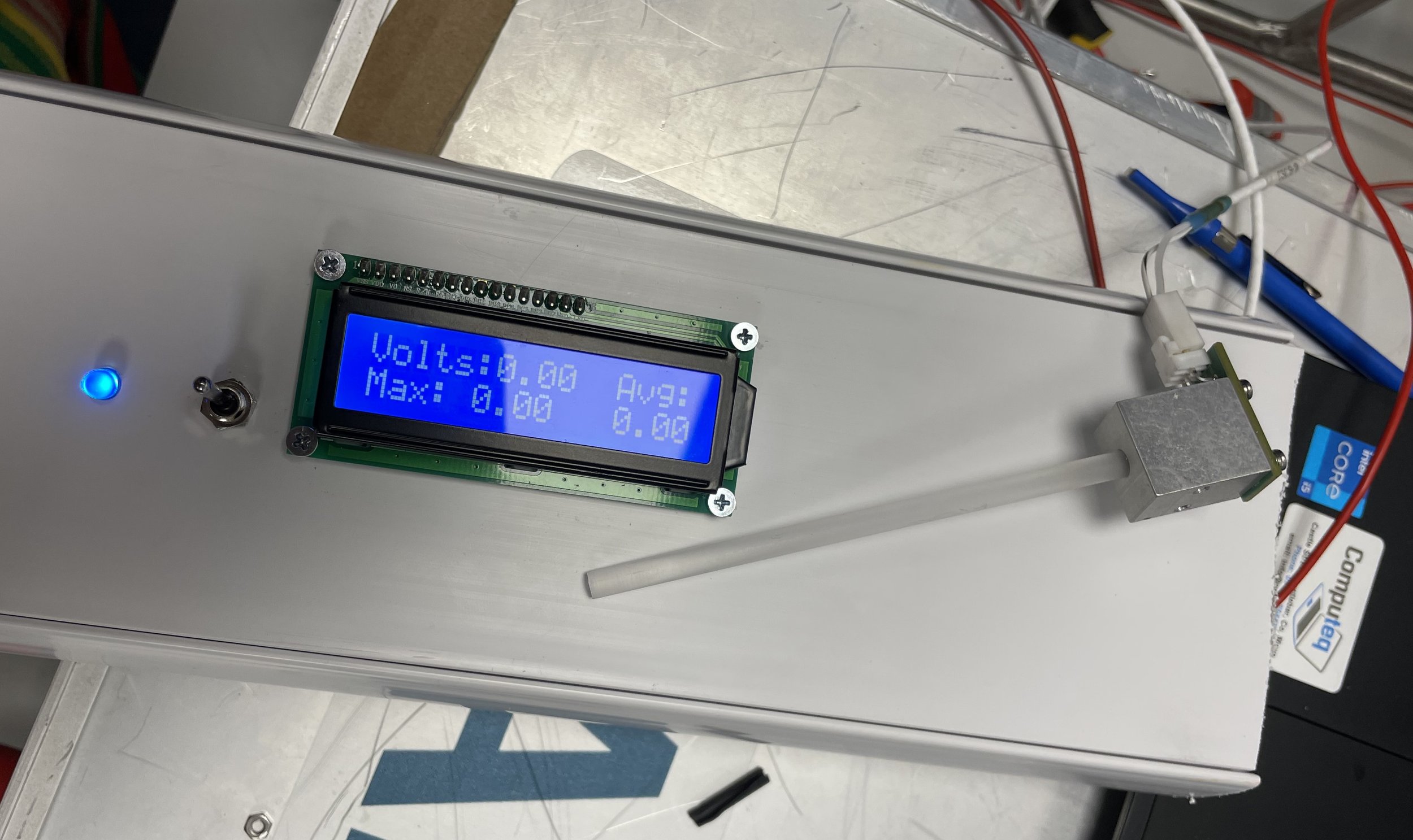
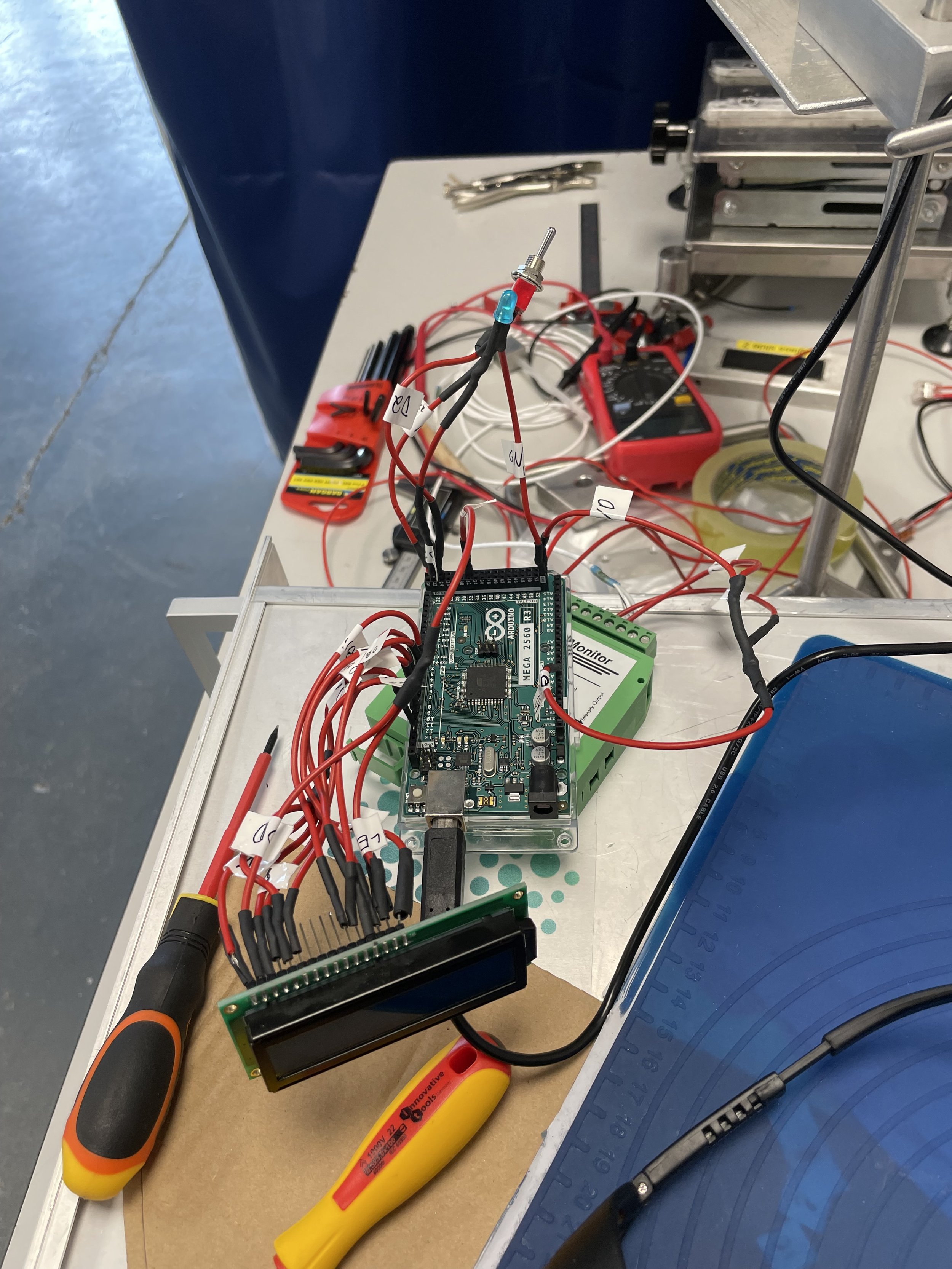
The image on the left is the electrical components of the sensor before they were mounted into the housing. The components of the system are an Arduino Uno board, a toggle switch, a blue LED, a 16x2 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), and the sensor hardware box (seen in green below the Arduino).
The way the sensor system works is as follows: First, you turn on the system using the toggle switch. Once the system is on, the blue LED and LCD will turn on indicating that the sensor is taking readings. The LCD displays the current voltage output of the sensor, the max voltage output, and the average voltage output from the last 20 readings above zero. Flipping the toggle switch resets the sensor and resets the maximum reading down to zero. The voltage output was correlated to readings in Joules through experimentation using other sensors and the quartz rod. The device was coded in Arduino and is powered by a separate 12V PSU box.
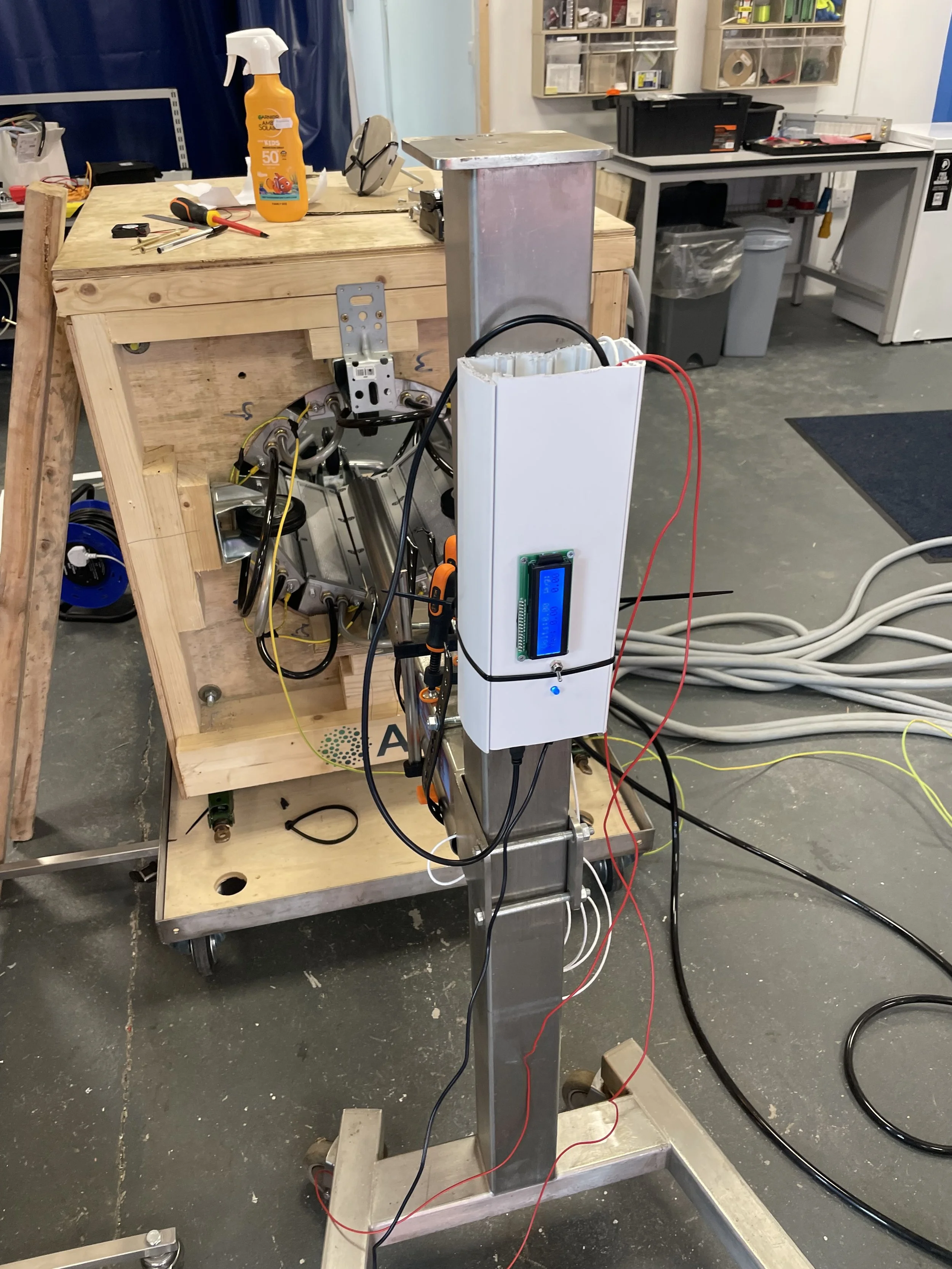
Quartz Rod In Use
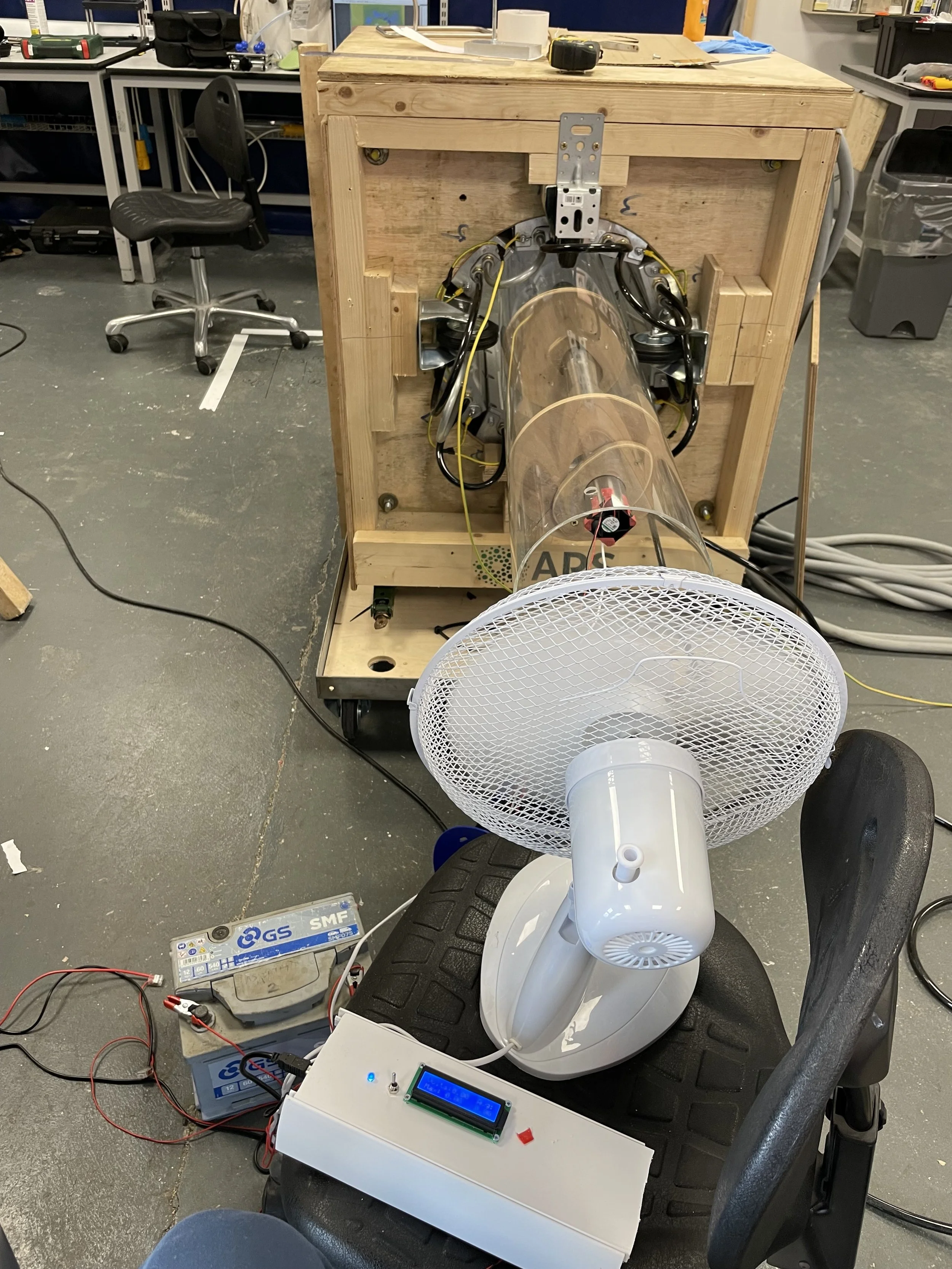
Here you can see the housing for the quartz rod mounted on the back of a metal cart that we used for testing. The quartz rod itself along with the aperture is mounted at the end of a stainless steel tube mounted to the cart that has been placed in the center of the light tunnel. the purpose of the stainless steel tube is to protect the wires from high temperatures. there is also a small fan mounted at the back of the tube to keep air flowing through and keep the temperature down.
Quartz Rod Sensor in Action
Below you can see a video of the quartz rod mounted on the cart inside the tube of lights and you can see how the values are displayed. The lights are turned on and the readings, which is a measure in volts, is displayed on the LCD screen.
Further Testing
Here you can see another testing configuration. The quartz rod is mounted in a rotationg tube using wooden plates that allow us to change the distance from the rod to the center of the tunnel and rotate it to different angles in order to map out the light intensity at different points in the tube.