milk-it-place
milk-it-place was the final product that my team and I designed in our Human-Centered Design and Innovation class in the fall of 2022 at Columbia University. The prompt was to design something that would help mothers and we decided to focus on breastfeeding issues that new mothers face, especially mothers who are returning to the workforce. The Team consisted of Natalie Wu (MS- Computer Science), Tiffany Lau (CC ‘24 - Financial Economics and Psychology), Max Wang (CC ‘23 - Economics), and myself.
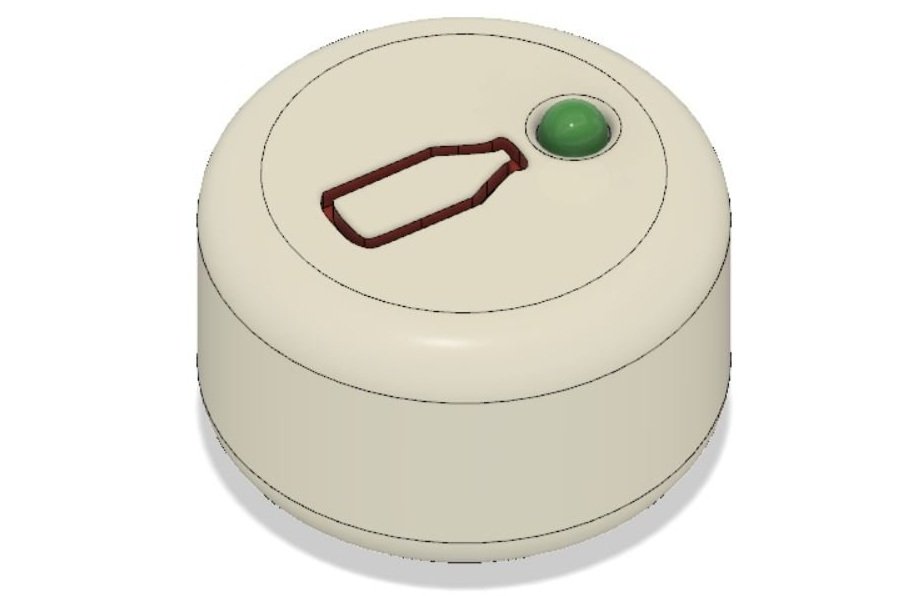
milk-it-place proprietary bottle caps
milk-it-place designed two proprietary caps that are a part of our product. One of the caps features a flow meter that is built in with a tube inlet that accepts the output tubes from standard breast pumps. This cap is able to measure the volumetric output of breast milk and output time from a breast pump that a mother is using to fill one of our milk-it-place bottles. The other cap features an electromagnetic system as well as an LED. The electromagnetic system works by having one magnet in the bottle cap and one agent on the top of the bottle. When the two magnets are in contact, the LED on top of the cap will show a green light, indicating that the bottle has been sealed since the milk was pumped in. If the seal has been broken, the LED illuminates red indicating that the milk may have been tampered with en route. The cap resets each time the bottle is emptied. I designed these caps in Fusion 360 for our team.
Flow-Meter, Output Sensing Cap
Here you can see how the output tube from a breast pump is inserted into our cap. The flow meter is built into the cap and the milk coming out of the tube flows through our small flow meter. the output data is then wirelessly uploaded into our app.
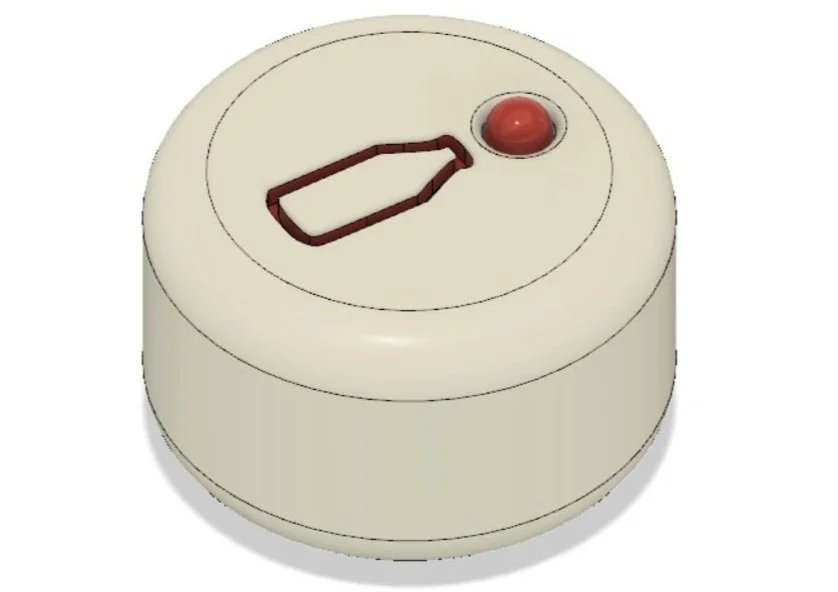
Seal-Sensing Cap with Green LED
This is our cap with the green LED illuminated indicating the bottle has been sealed since it was filled.
Seal-Sensing Cap with Red LED
This is our cap with the red LED illuminated indicating that the bottle has been opened since it was sealed.
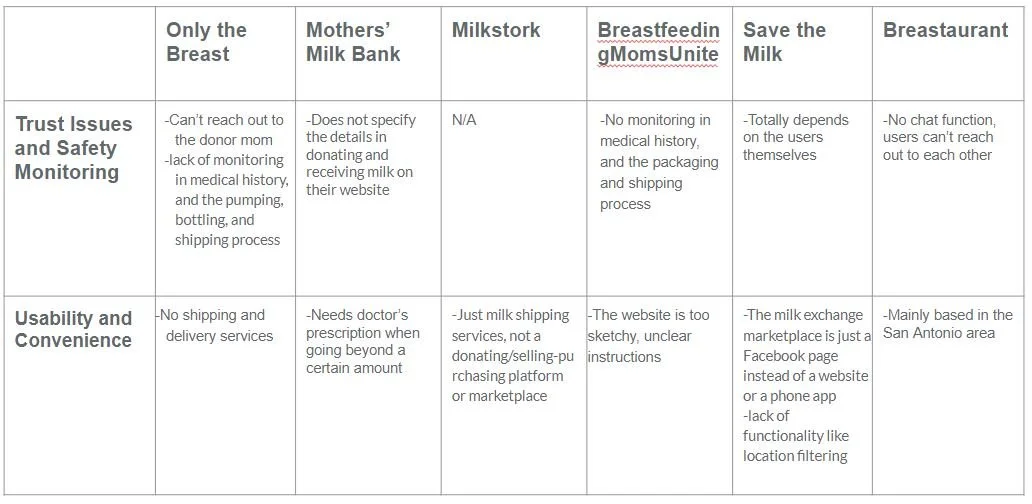
Our Solution Compared To The Competition
FAQs
Might mothers be hesitant to buy others’ milk online when it comes to their babies?
Yes, they might be which is why we included the following trust-building features to help remediate this issue:
Test strips and initial screening for mothers address the problem of contaminants and viruses such as HIV
Ability to video-chat potential sellers/star ratings and profile of each mother
Flow-meter monitoring output and ensuring mothers can tell if anything was added to their milk
Magnetic sensor (tests if the bottle has been opened since it was sealed)
milk-it-place collecting used bottles and bringing them to our warehouse to disinfect and clean them
If one mom is over-producing consistently, how will the credit system benefit them? They do not need milk from other moms, and probably want some compensation for their milk/work, so how would that work?
Rewards:
There will be a feature on the app that allows mothers to exchange their credit for rewards such as gift cards with partner organizations
How would you prevent the spread of HIV through commonly shared breast milk?
Initial Health Screen:
Donor moms will also have to go through an initial health screening process and will go through this screening annually (this isn’t a hassle since most moms stop producing milk after a year)
How do you make sure the milk is real breast milk and not cow’s milk?
Pumping vs Dumping:
Our flow meter will measure how much milk is pumped through the inlet hole and will not measure any milk that is simply dumped in. Mothers can confirm the same volume that was pumped in is the same amount that was delivered, using the volumetric marks on our bottles, to ensure that it was not tampered with
How do the test strips work?
Test strips will be a lateral-flow assay, similar to commonly used covid tests. These tests have specific reagents and colored particles that will bond to certain contaminants and result in a colored line showing up on the test trip if contaminants are present in the sample, such as bacteria or alcohol.